Figure 2.
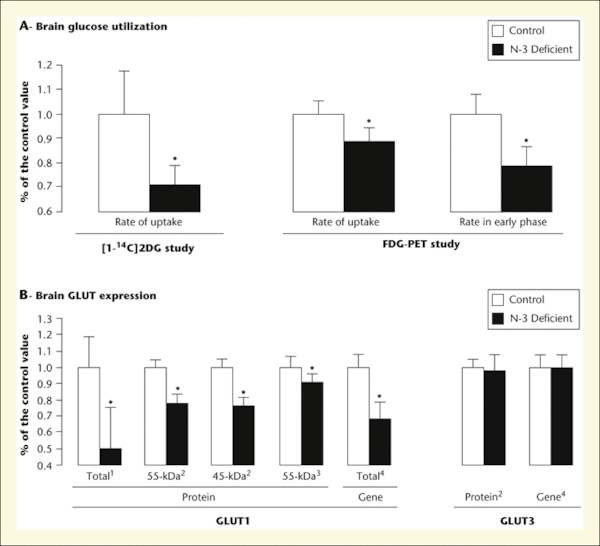
Download original image
Impact of n-3 PUFA deficiency on glucose utilization (Part A) and GLUT expression (Part B) in the rat brain at rest. Part A. Cerebral glucose utilization was evaluated in the frontal cortex using the semiquantitative autoradiographic [1-14C] 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) method (Ximenes et al., 2002), and in the whole brain using the [18F]-2DG positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) (Harbeby, 2011). The FDG uptake was calculated both during the later plateau and the early phases of the kinetic. Part B. 1 The level of total GLUT1 staining was measured in the fronto-parietal cortex by immunocytochemistry on 30 μm coronal sections (Ximenes et al., 2002). 2 GLUT1 and GLUT3 protein levels were assayed by western blotting on samples of cerebral cortex homogenates (GLUT1 45-kDa and GLUT3) and microvessels (GLUT1 55-kDa) (Pifferi et al., 2005). 3 Quantification of GLUT1 55 kDa was also performed by determining the specific binding of cytochalasin B to GLUT1 on total membranes prepared from isolated microvessels (Pifferi et al., 2007). 4 Level of mRNA expression of GLUT1 gene (Slc2a1) determined by real-time PCR TaqMan Low-Density Array (TLDA) technique (Harbeby et al., 2012). Bars represent means ± SEM (n = 6-8 rats/diet group). * Statistically different from the control rats (P < 0.05).
Les statistiques affichées correspondent au cumul d'une part des vues des résumés de l'article et d'autre part des vues et téléchargements de l'article plein-texte (PDF, Full-HTML, ePub... selon les formats disponibles) sur la platefome Vision4Press.
Les statistiques sont disponibles avec un délai de 48 à 96 heures et sont mises à jour quotidiennement en semaine.
Le chargement des statistiques peut être long.




