Fig. 1
Download original image
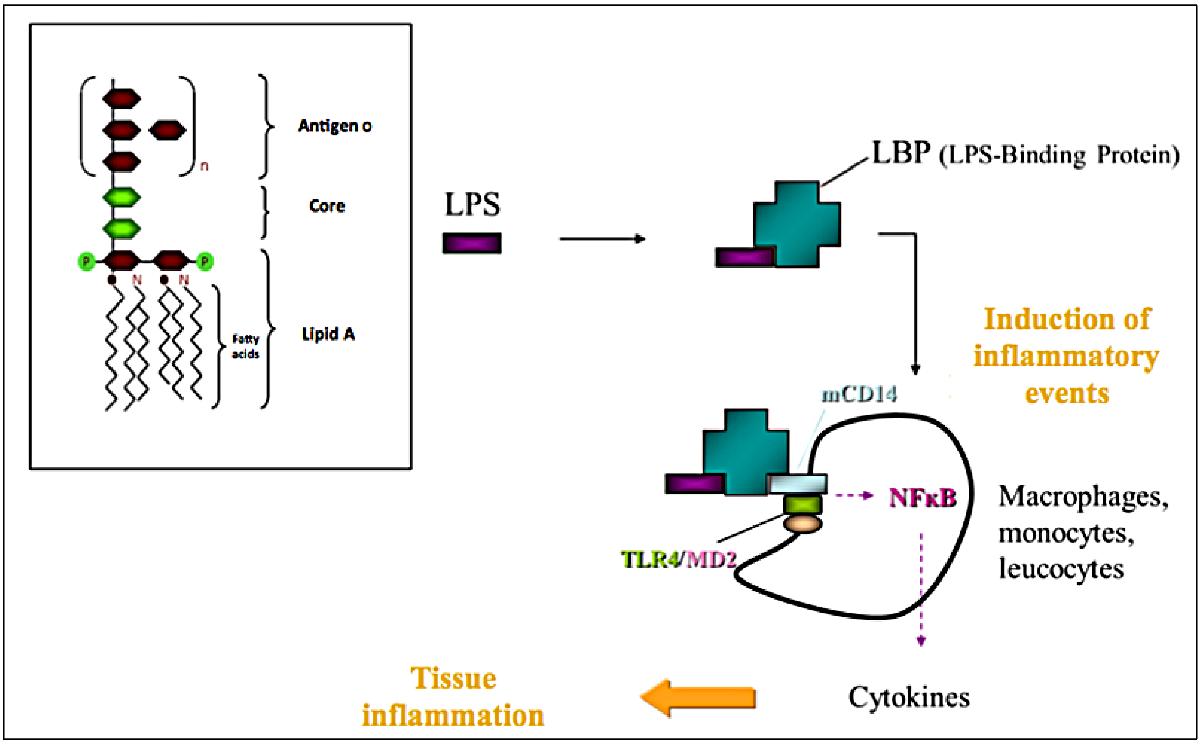
Pro-inflammatory events induced by plasma lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Adapted from Laugerette et al. (2011); Vors et al. (2014). If reaching the bloodstream, LPS are taken up by a specific transport glycoprotein, the lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), towards immune cells (such as macrophages). Immune cell activation requires a specific molecular complex consisting of the membrane form of the cluster of differentiation 14 (mCD14), the Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) and the Myeloid Differentiation protein-2 (MD2). The mCD14 is a glycoprotein able to bind the LPS-LBP complex, which can then fix on the TLR4 receptor and the co-receptor MD2 and then mediate signal transduction via the activation of NF-κB (Nuclear Factor-κB). This signalization cascade results in the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, etc.).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.




