Fig. 4
Download original image
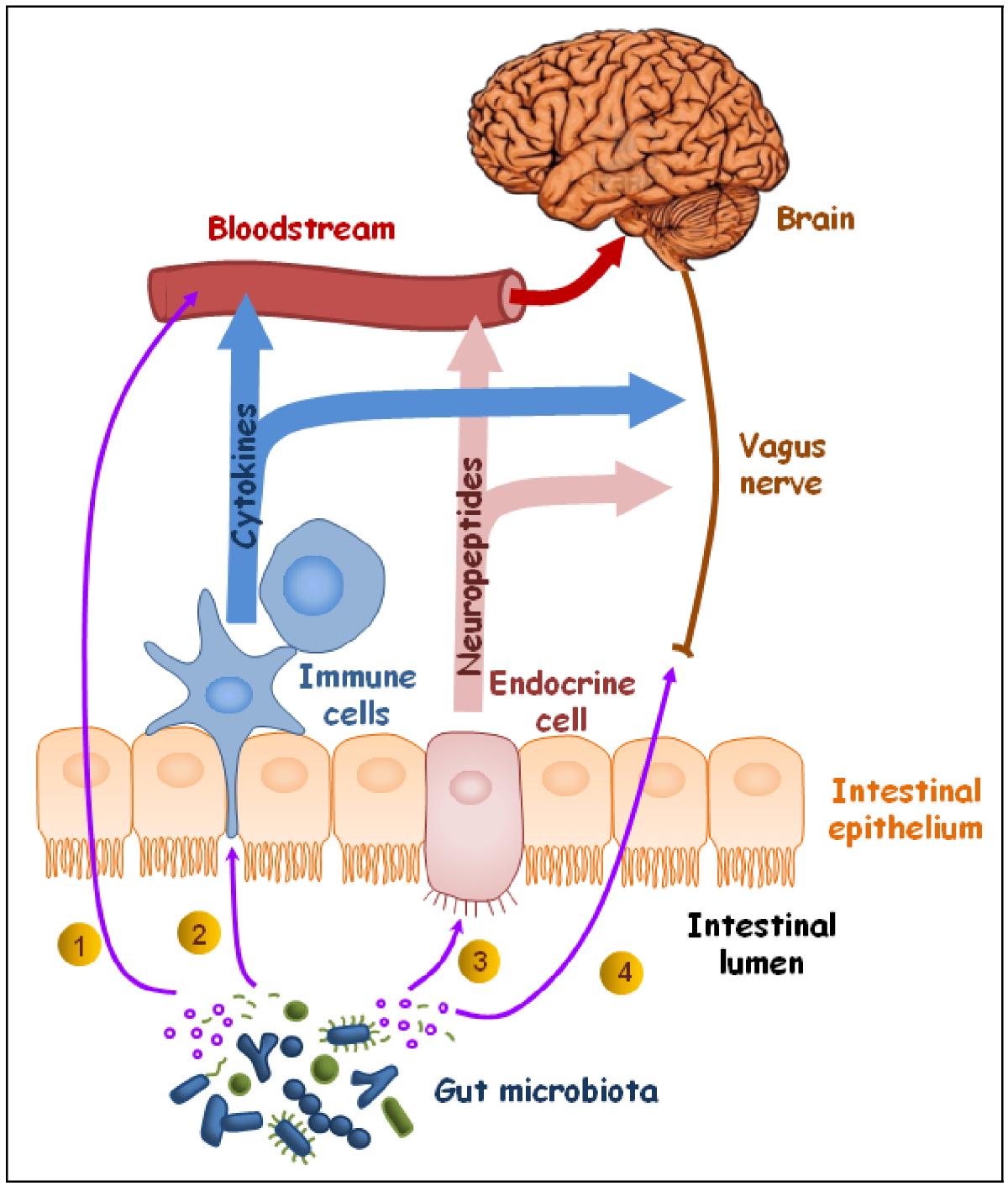
Pathways involved in communication between the gut microbiota and the brain. Effective bacterial molecules can be metabolites released in the gut lumen (e.g. fermentation products or neurotransmitter-like molecules, here in green) or cell structural components (e.g. lipo-polysaccharides of the cell wall, here in purple). They can reach the brain via the systemic circulation (1), signal the immune system and trigger the production of cytokines (2), signal the entero-endocrine cells and trigger the production of neuropeptides (3), or activate the vagal and enteric nervous system afferent fibers (4).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.




